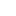
获取特定标签的数据
如何使用Python进行网络爬虫开发
随着互联网的快速发展,网络爬虫技术在数据分析、网站信息收集和自动化测试等领域发挥了重要作用,本文将详细介绍如何使用Python编写基本的网络爬虫程序,以实现从网页中抓取所需数据。
安装必要的库
确保你的环境中安装了Python,并且已经添加了pip命令行工具(如果还没有的话),你需要安装一些常用的网络爬虫库,如requests用于发送HTTP请求,以及BeautifulSoup或lxml用于解析HTML文档。
pip install requests beautifulsoup4 lxml
设置请求头
大多数网站对访问频率有限制,通过设置合适的User-Agent头可以绕过这些限制。
import requests
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/58.0.3029.110 Safari/537.3'
}
response = requests.get('https://www.example.com', headers=headers)
print(response.text)
解析HTML
利用BeautifulSoup来解析HTML文档中的结构化数据。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
for link in soup.find_all('a'):
print(link.get_text())
# 或者获取所有链接
for link in soup.find_all('a', href=True):
print(link['href'])
处理复杂页面
某些网页可能包含JavaScript动态加载的内容,这时就需要使用Selenium来模拟浏览器行为。
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
driver.get('https://www.example.com')
# 使用WebDriverWait等待元素出现
element = WebDriverWait(driver, 10).until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.ID, "search_field")))
# 发送表单数据
element.send_keys("example")
element.send_keys(Keys.RETURN)
# 读取页面源码
page_source = driver.page_source
driver.quit()
# 解析并提取数据
soup = BeautifulSoup(page_source, 'html.parser')
for item in soup.find_all('div', class_='item'):
print(item.get_text())
数据存储与处理
爬取到的数据通常需要保存起来供后续分析或使用,可以使用数据库(如SQLite、MySQL)或者文件系统来存储数据。
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect('data.db')
c = conn.cursor()
c.execute('''CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS items (id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, content TEXT)''')
items = [
('Item 1', 'Description of Item 1'),
('Item 2', 'Description of Item 2'),
]
for i, (title, desc) in enumerate(items):
c.execute("INSERT INTO items (id, content) VALUES (?, ?)", (i+1, desc))
conn.commit()
conn.close()
步骤介绍了如何使用Python编写简单的网络爬虫,包括基本的HTTP请求、HTML解析、以及处理复杂页面的能力,实际应用中,还需要考虑异常处理、并发操作、登录验证等更复杂的场景,希望本篇文章能帮助你开始自己的网络爬虫之旅!

 上一篇
上一篇